New SLAM-Based Super Station RTK Solution Has Been Launched
RTK measurement usually refers to mobile measurement devices using RTK technology. Use a GNSS receiver to connect to the CORS system through a radio station or network to perform RTK positioning. At the same time, a centering rod with a specified length is used to collect real-time high-precision coordinates of the bottom point of the centering rod, such as the collection of control point coordinates, fragment points, drawing root points, etc., and drawing lofting, etc.
Traditional RTK
Traditional RTK measurement uses a centering pole, which requires strict vertical alignment of the GNSS antenna phase center and the measured point. Therefore, a leveling bubble is usually installed on the centering rod and strictly calibrated in the laboratory.
When collecting data with traditional RTK, for points to be measured with upper structures such as room corners, because the GNSS receiver host has a certain size, it is usually impossible to accurately collect plane positions.
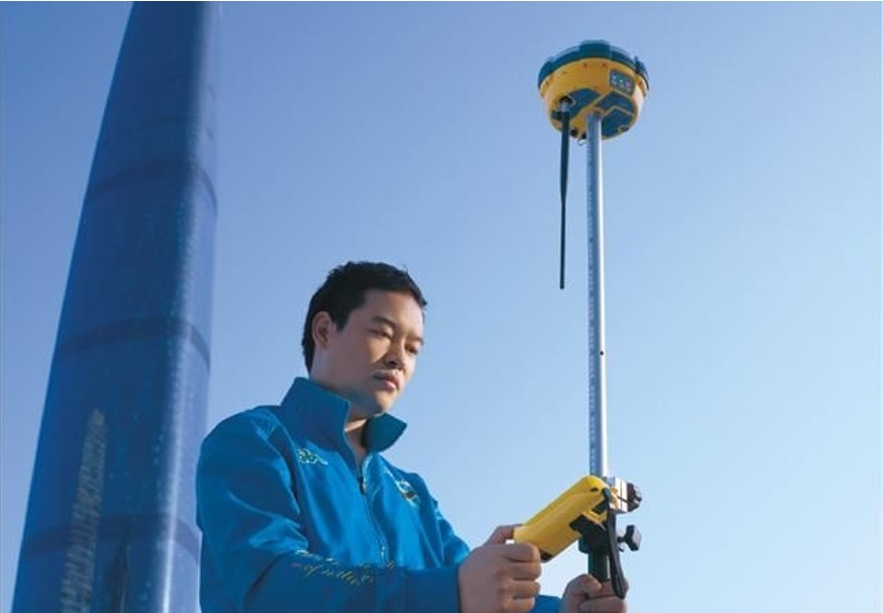
Inertial RTK
In order to solve the problem that traditional RTK cannot perform tilt measurement, professional surveyors have developed GNSS receivers with built-in inertial navigation. The receiver can correct the distance from the GNSS phase center to the measured point based on the tilt angle and direction of the centering pole, and can accurately collect points with side interference. However, like traditional GNSS receivers, inertial navigation RTK can only collect in environments with GNSS signals. It is still unable to perform effective collection in environments without GNSS signals such as inside buildings and under eaves.
Image RTK
In order to solve the data collection problem of points in areas without GNSS signals such as under the eaves, image RTK came into being. Image RTK is a built-in camera module on the GNSS receiver. It can capture the point to be measured in the area where the GNSS signal can be received according to the forward intersection method of photogrammetry, and obtain the coordinates of the point to be measured through multi-angle image intersection or conduct stake out.
Laser RTK
Laser RTK refers to a device that installs a laser rangefinder on a GNSS receiver and uses laser pointing to collect and stake out points. Laser RTK can directly illuminate the point to be measured through the laser without using a centering rod, and at the same time measure the distance information from the device to the point to be measured. Based on the pose information provided by the high-precision inertial navigation and GNSS built into the fuselage, the solution to be measured is obtained. Point coordinates.
Image RTK and laser RTK solve the 10-meter edge measurement from GNSS signal to no signal but are unable to do anything for deeper areas without GNSS signal, such as the measurement of the bottom of complex interchange systems, indoor and outdoor parking lot measurements, etc.

Traditional RTK

Inertial RTK

Image RTK
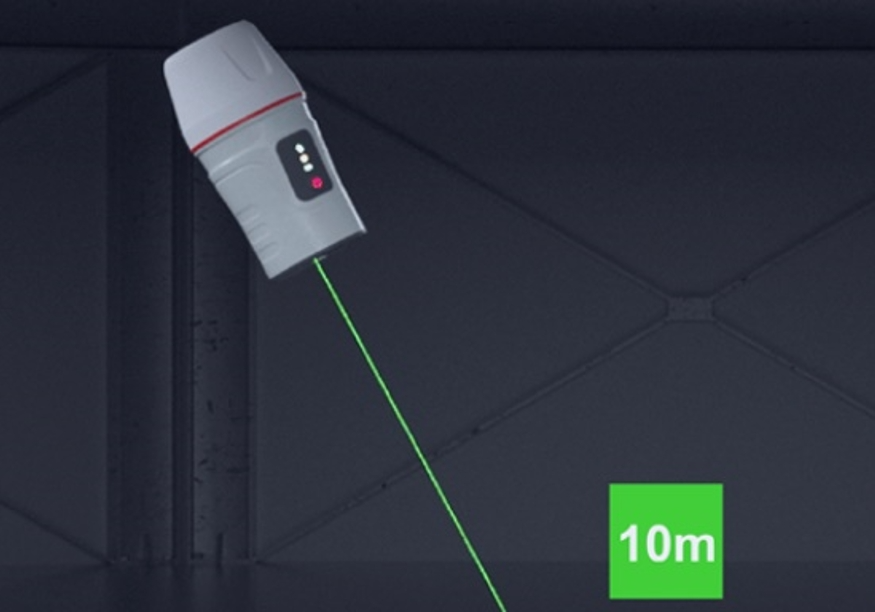
Laser RTK
Introduction
Superstation RTK refers to GNSS RTK receiver equipment that uses SLAM technology to achieve navigation measurements on traditional RTK. In this device, laser SLAM technology is introduced into the traditional GNSS receiver, and laser SLAM's powerful environmental perception capabilities and map construction functions are used to achieve high-precision position navigation and accurate real-time point measurement. In an environment with GNSS signals, RTK equipment will mainly rely on GNSS signals for point measurement or stakeout, and make positive corrections to the laser SLAM odometry; after RTK equipment enters an area without GNSS signals, it will rely on laser SLAM for measurement. Position navigation continues to output high-precision position information.
Based on this technical direction, we proposed a solution to realize super-station RTK using SLAM2000 handheld lidar scanner + S-RTK100 multi-function portable RTK module.
SLAM2000 System Introduction
SLAM2000 is new generation handheld lidar scanner. It uses a non-repetitive scanning laser sensor, self-developed high-precision inertial navigation, and a 12-megapixel camera. It has the capabilities of high-precision point cloud mapping and high-precision navigation and positioning.
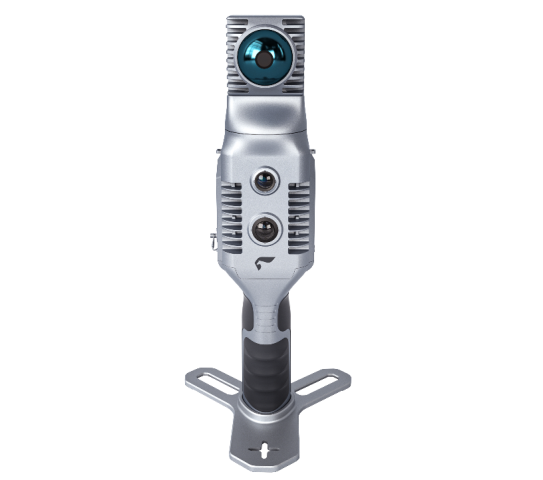

S-RTK100 system introduction
S-RTK100 adopts a five-star and sixteen-channel board module. It can be used with SLAM products or can be used as a separate GNSS receiver for data collection, achieving centimeter-level absolute accuracy data collection.
Usage
Superstation RTK is mainly composed of GNSS receivers, SLAM equipment, centering poles and APPs, and there is no need to add other hardware equipment.
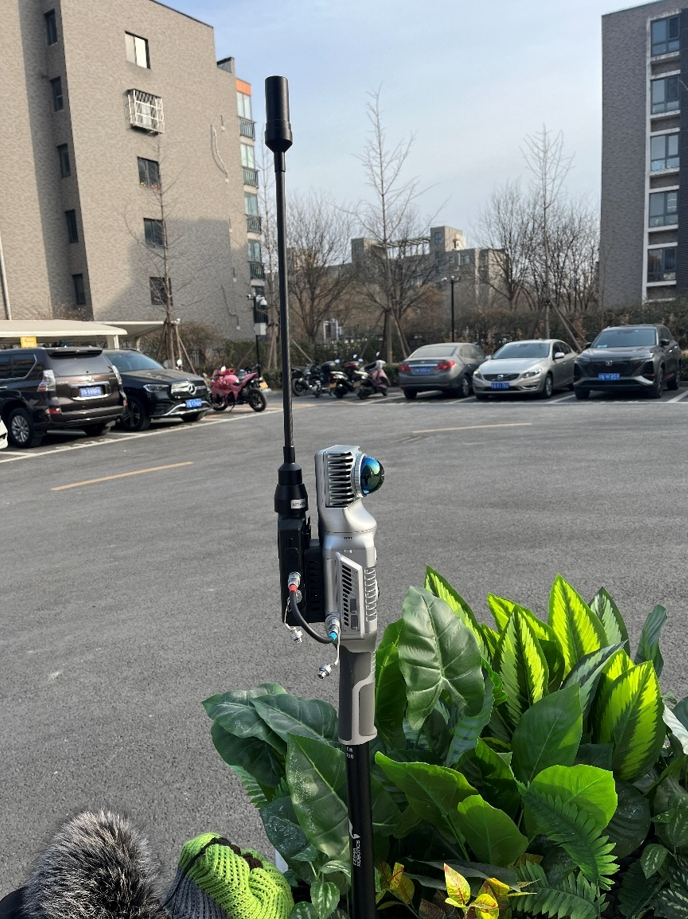

The overall workflow is as follows:
1) Connect RTK equipment, SLAM equipment, alignment poles and other equipment to complete the super-station RTK assembly, and control and collect through the mobile APP.
2) During the initialization process, it is necessary to ensure that the superstation RTK is turned on in an area without GNSS obstruction. Use the mobile APP to set the CORS system, set pole height and other parameters. After the RTK obtains the fixed solution, turn on the SLAM equipment and create a new project.
3) During the acquisition process, whether in an area with GNSS signals or in an area without GNSS signals, RTK can perform normal acquisition, tilt mode acquisition, inverted mode acquisition, etc.; it can be used for situations where the GNSS signal is severely blocked or where there is no GNSS signal at all. coordinate collection or stakeout in areas such as under woods, under eaves, indoors, underground spaces, etc.
4) Export the collected coordinate point data for further production of required surveying and mapping results.
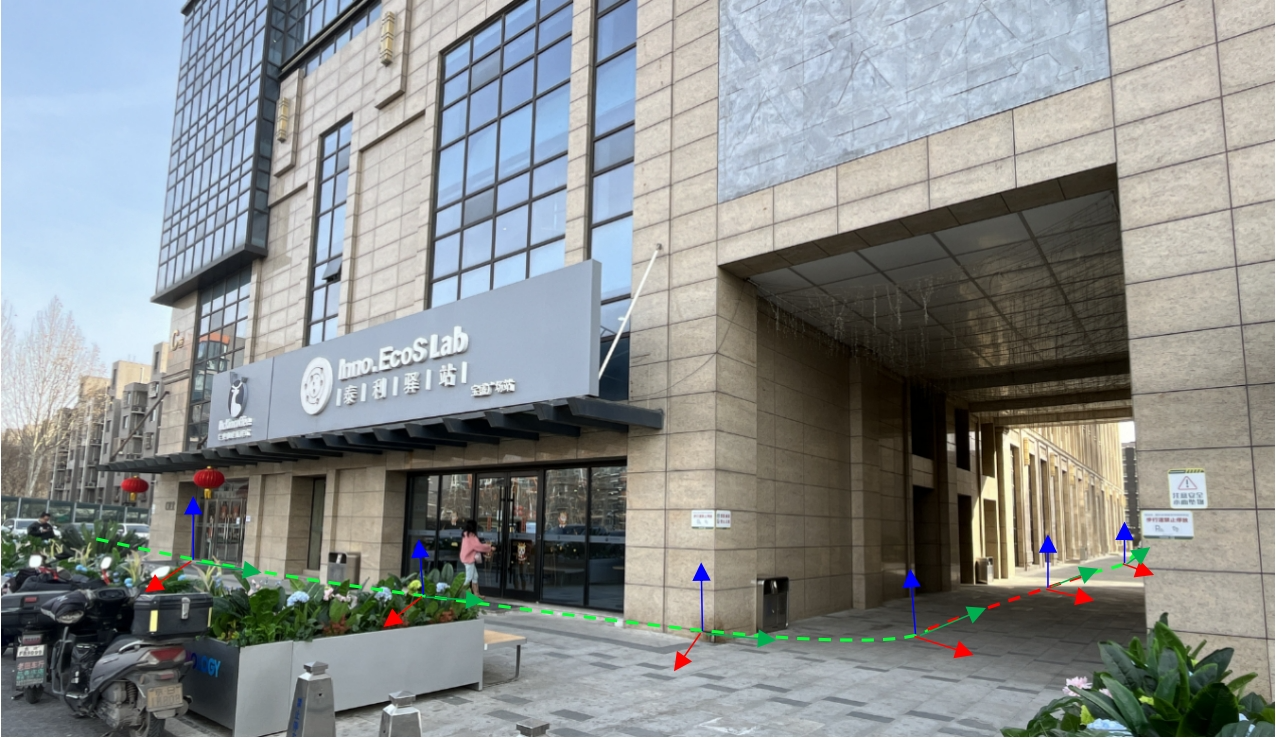

Collection diagram
As shown in the figure above, the superstation RTK collects position information based on the RTK data obtained by GNSS in a normal outdoor environment (green track), and at the same time corrects the pole height and inclination based on the SLAM posture. If it is caused by tilt or inversion, If the GNSS signal is blocked, the laser SLAM odometry can continue to perform position and attitude navigation; after entering a GNSS-free environment (red track), the GNSS signal is lost, and the laser SLAM can continue to perform position and attitude navigation and accurately obtain the position of the point to be collected. Coordinate information; when returning to an outdoor environment from an environment without GNSS signals, data collection can be continued continuously. If the area without GNSS signals is large, you can ensure the accuracy of the collected coordinates by going outdoors several times to receive a section of GNSS data and then returning it indoors. You can also perform post-processing as needed to further improve the data accuracy.
As mentioned earlier, the current RTK measurement methods that rely on GNSS receivers and other sensors mainly include traditional RTK, inertial navigation RTK, image RTK, laser RTK, etc.
Traditional RTK uses a GNSS receiver as the main body for coordinate measurement or stakeout; inertial navigation RTK has built-in inertial navigation equipment and can perform centering pole tilt measurements; image RTK is based on a vision system and can perform forward intersection, collect the coordinates of the point to be measured through images, or provide guidance Carry out point stakeout; laser RTK uses laser pointing and ranging to collect or stake out the coordinates of laser points. At the same time, laser RTK must also use an inertial navigation system. The above multiple modes can be combined and integrated with each other to achieve more application functions.
In order to verify the feasibility of super-station RTK, the combined solution of SLAM2000+S-RTK100 was used for verification, and data were collected on the ground buildings, features, lobbies, and underground garages in the Beijing Baosheng Plaza area, and a surveying and mapping result map was made.
Baosheng Plaza is a building with 1 underground floor and 9 floors above ground. The whole building is in the shape of a square. Some areas have corridors. The overall floors are high. The shops on the ground floor have physical eaves. It is impossible to completely obtain all the points to be measured using traditional RTK, and it is impossible to Direct indoor and underground measurements. It is usually necessary to use a total station or other means for measurement based on traditional RTK, but using the super-station RTK solution can complete the measurement in one go and ensure the accuracy of surveying and mapping.
Schematic diagram of Baosheng Plaza
Initialization
Install SLAM2000 + S-RTK100 on a dedicated single pole, turn it on and perform CORS settings, SLAM initialization and other parameter settings on the device.
Data Collection
After the initialization is completed, data collection can be carried out. During the collection process, point collection is carried out through the mobile APP. Whether you are in an area with GNSS signals or entering an area without GNSS signals, you can use superstation RTK for regular measurements, tilt mode measurements, inverted measurements, etc. After the collection is completed, the list of indoor and outdoor coordinate values can be directly output.
Draw Survey Results
Plot indoor and outdoor broken step points collected using superstation RTK to generate line drawing results. In the same set of data, the interior of the building and the underground garage can be directly drawn, and a complete set of ground and underground drawings of Baosheng Park can be obtained directly.
Super station RTK is newly launched SLAM+RTK working mode. It is mainly used for obtaining or setting out absolute coordinates of points in normal environments and in scenarios with no GNSS signals or no visibility. Relying on SLAM technology, it effectively simplifies the traditional RTK operation process, expands the scope of RTK use, and provides new equipment options for engineering measurement.
- Reinforcement Learning Enables Bipedal Robot to Conquer Challenging Terrain
- Drones for 3D Indoor Exploration-Cultural Relics Protection and Indoor Survey
- Industry Application: Intelligent Unmanned Operation Solutions for Lakes – Rapid Deployment for Continuous Protection
- High-Altitude Cleaning Case Introduction - Drone Spraying and Cleaning
- New Performance: SLAM Handheld Lidar Scanner + External Panoramic Camera New Combination